Major cities like New Orleans sink inches yearly while others battle increasingly severe floods. Historic landmarks, homes, and neighborhoods could vanish beneath the waves by 2050.
Our analysis covers 15 major global cities fighting to stay above water. We’ll explore how each location faces unique challenges – from Amsterdam’s innovative flood barriers to Bangkok’s creative water management solutions.
This isn’t a distant problem. Many coastal residents already wade through flooded streets during their daily commute. The future of these cities depends on how we respond to this growing crisis today.
#1. Charleston, South Carolina, Could Be A ‘Half-Drowned Ghost Town’ By 2050
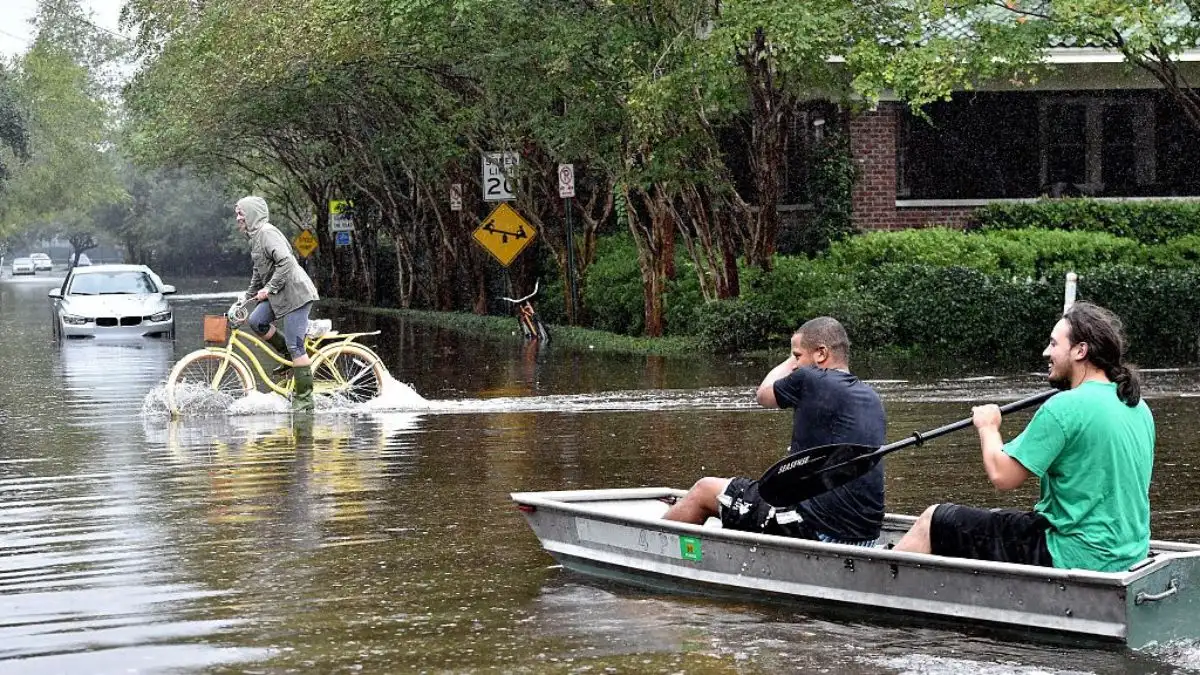

Rising sea levels severely threaten Charleston’s historic charm and vibrant community. Local experts warn that by 2050, much of this beautiful coastal city might vanish beneath the waves. The combination of intense storms and higher tides has already started showing its effects on daily life.
Streets regularly flood during heavy rains, forcing residents to adapt their routines. Scientists project that a 12-foot sea level rise would submerge about 75% of the area underwater. Many neighborhoods face difficult choices about their future as water continues creeping inland. The city’s infrastructure struggles to handle the increasing flooding episodes. Storm drains often back up during high tides, creating problems even on sunny days.
Local authorities have started implementing flood prevention measures, but some worry these efforts might not be enough. Community leaders are working to preserve historical buildings while planning for an uncertain future. Some residents have already started moving to higher ground, though many remain hopeful about finding solutions.
#2. Miami Will Likely Be Underwater By The End Of The Century
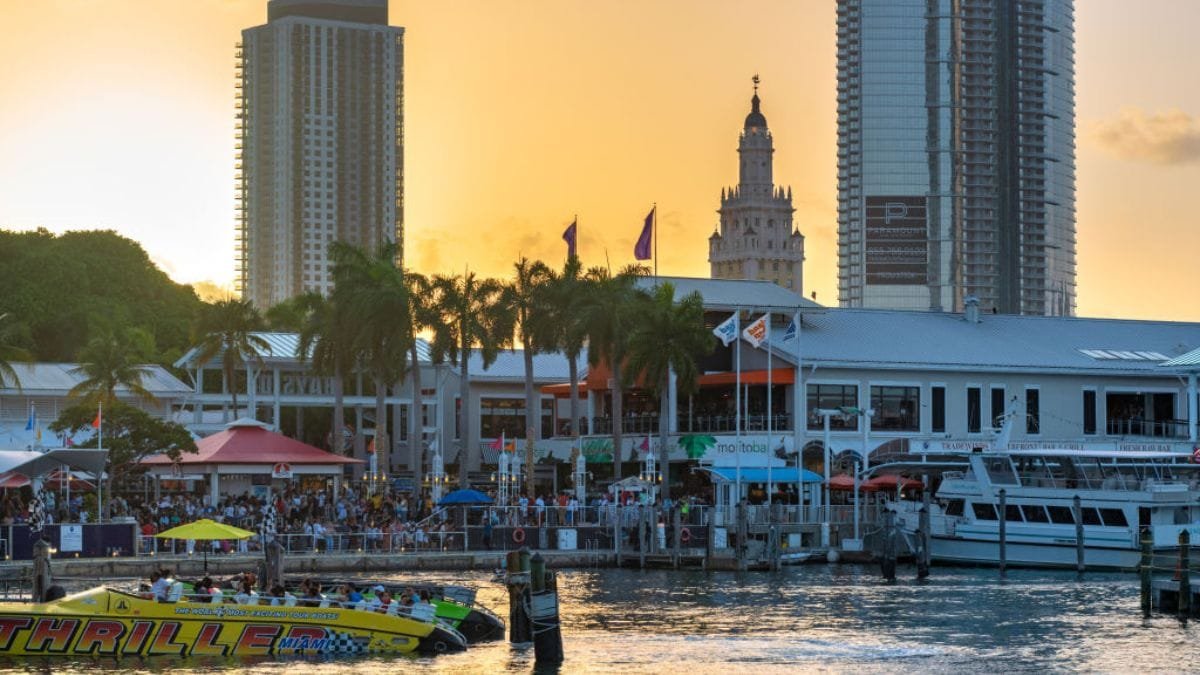

Water threatens to reshape Miami’s famous coastline dramatically in coming decades. Recent studies show that about 12,000 homes in Miami Beach face serious flooding risks within 30 years. The estimated value of these vulnerable properties reaches $6.4 billion.
Saltwater has begun seeping into underground freshwater supplies, causing additional concerns for residents. Local officials spend millions each year raising roads and installing powerful pumps. Flooding happens more frequently now, even during regular high tides without storms. Property values could start dropping as flooding risks become more apparent to buyers.
Scientists warn that the city’s limestone foundation makes it particularly vulnerable to rising waters. Miami-Dade and Broward county residents face some of the highest flooding risks in America. The city council has proposed ambitious plans to raise buildings and improve drainage systems. However, engineering solutions might only buy time rather than provide permanent protection.
#3. Venice, Italy, Is Building A Flood Barrier But Is Way Behind On Construction
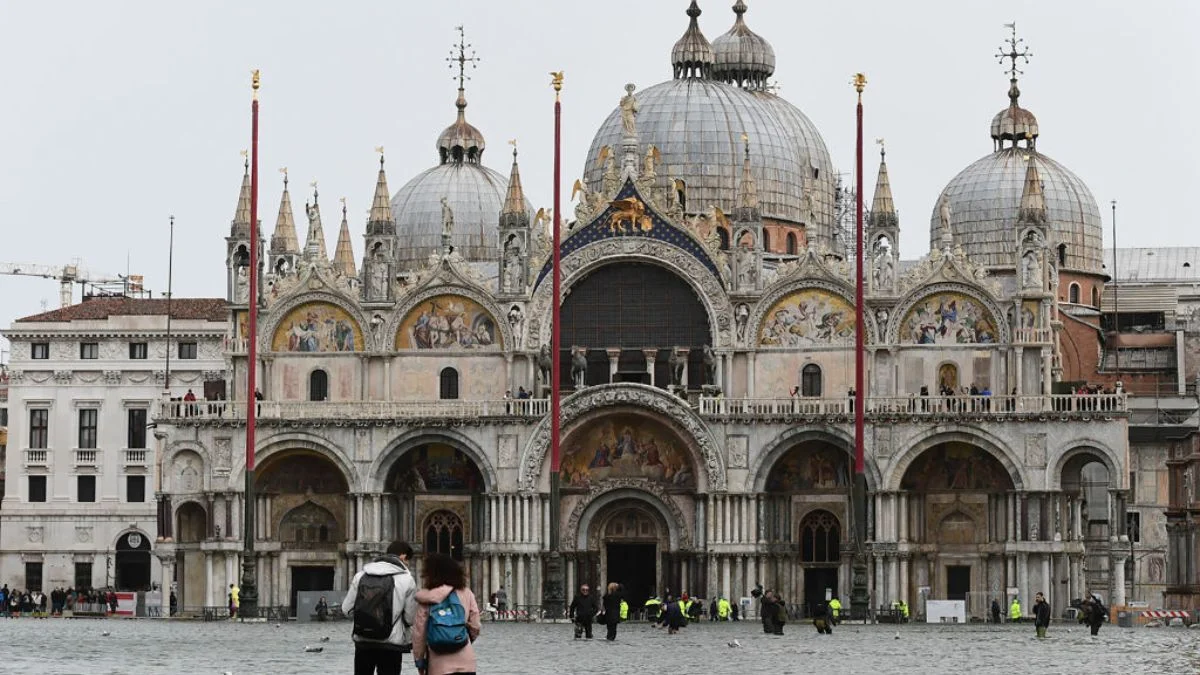

Venice’s battle against water grows more challenging each passing year. The ancient city sinks approximately one inch annually while sea levels continue rising around it. A massive flood barrier project started in 2003 remains unfinished despite its original 2011 completion date. Tourists and locals regularly wade through flooded streets and squares during high tides.
The $6.5 billion barrier project faces constant delays and technical challenges. Historical buildings suffer increasing damage from saltwater exposure. Local businesses must frequently close during flooding events, affecting the city’s tourism-based economy. Engineers work to strengthen building foundations while preserving Venice’s unique architectural heritage.
The delayed barrier project symbolizes the complexity of protecting historic cities from rising seas. Recent flooding events have reached levels not seen in decades, highlighting the urgency of completing protective measures. The city’s future depends largely on successfully finishing and maintaining these ambitious engineering projects.
#4. Houston Is Prone To Flooding Even Though It’s Not A Coastal City

Houston faces unique flooding challenges despite its inland location. The city sinks about two inches yearly due to excessive groundwater pumping. Hurricane Harvey revealed how vulnerable the city’s infrastructure is to extreme weather. Around 135,000 homes suffered damage during that single storm event. Urban development has replaced natural drainage areas with concrete and asphalt.
The combination of sinking land and intense rainfall creates dangerous flooding situations. Low-lying neighborhoods experience repeated flooding during major storms. City planners work to create more green spaces that can absorb excess water. The rapid growth of Houston has outpaced its ability to manage stormwater effectively.
Local authorities now require new developments to include better drainage systems. Residents in flood-prone areas struggle with rising insurance costs and property values. The city continues searching for solutions to protect its growing population from future floods.
#5. Atlantic City Is Very Vulnerable When Hurricanes Hit

Atlantic City’s gambling paradise sits precariously close to rising seas. Hurricane Sandy showed just how vulnerable this entertainment hub is to powerful storms. Nearly 80% of the city went underwater during that devastating weather event. Storm surges pushed water levels up to eight feet in some areas. About 40,000 residents face serious flooding risks over the next century.
The famous boardwalk requires constant maintenance to withstand regular flooding. Casinos and hotels have started implementing their own flood protection measures. Beach erosion threatens the city’s main tourist attraction. Emergency response teams regularly practice evacuation procedures for future storms. The combination of low elevation and exposed coastline makes the city particularly susceptible to flooding.
Local authorities have begun planning for long-term adaptation strategies. Some neighborhoods might need to be abandoned as water levels continue rising. The city’s economy depends heavily on finding ways to protect its valuable coastal infrastructure.
#6. New Orleans Is Sinking Two Inches Annually
Life in this vibrant cultural hub grows more challenging each year due to the sinking ground beneath. Water surrounds the city on multiple sides, creating unique risks for residents. Built on a river delta, some areas already sit 15 feet below sea level. NASA researchers discovered the alarming rate of subsidence in their 2016 report. Local neighborhoods face regular flooding even during moderate rainfall.
The destruction of protective wetlands has left the area more exposed to storms. Groundwater pumping and natural soil compression contribute to the ongoing problem. Memories of Hurricane Katrina’s devastation still influence city planning decisions. Engineers work constantly to maintain and improve the levee system. Scientists predict most of the city could vanish beneath the waves by 2100.
Families must decide whether to stay and adapt or relocate to safer ground. Community leaders struggle to preserve the unique culture while protecting residents from increasing flood risks. Local authorities have implemented strict building codes to help structures withstand water damage.
#7. Boston May Be Partially Submerged By 2100
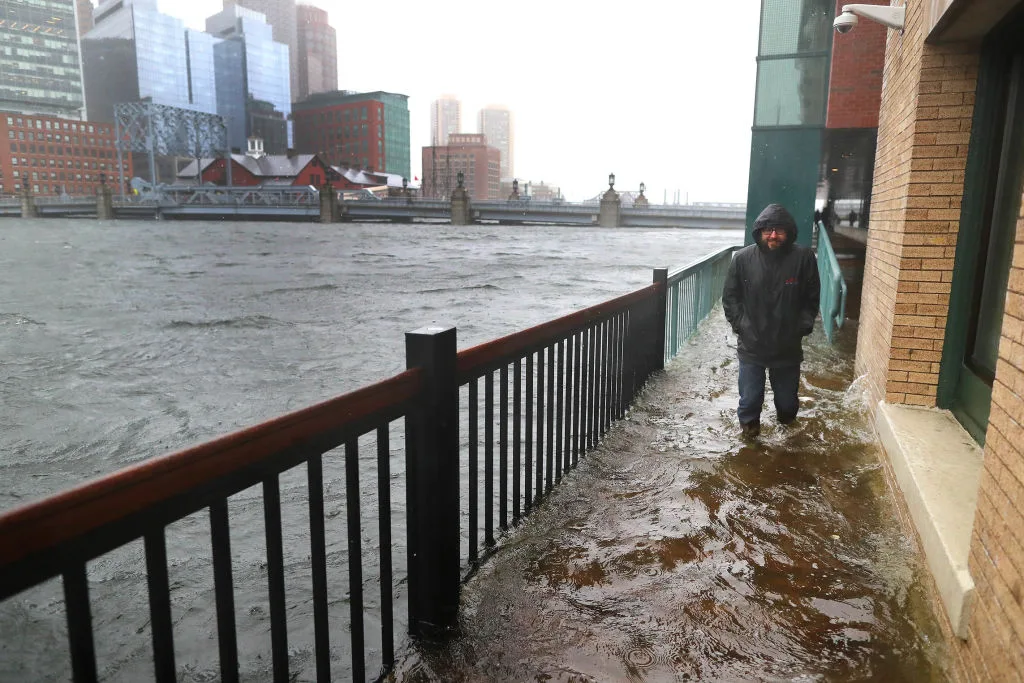

Water threatens to reshape Boston’s historic neighborhoods in coming decades. NOAA forecasts suggest sea levels around the city will rise approximately six feet. One in six homes faces serious flooding risks as waters continue rising. Storm surges already cause problems in low-lying areas of the city. Local authorities have started planning extensive flood protection measures. The famous harbor area particularly concerns city planners and engineers.
Historical buildings need careful protection from increasing flood risks. Scientists warn that at least one major flood will likely occur in the next 30 years. Community meetings often focus on how to preserve neighborhood character while adapting to rising waters. The city’s infrastructure requires significant upgrades to handle future flooding.
Residents in vulnerable areas watch property values fluctuate with each new forecast. Urban planners work to create innovative solutions for protecting the city’s heritage. The combination of rising seas and more frequent storms poses significant challenges.
#8. Virginia Beach’s Location Makes It Particularly Susceptible To Flooding
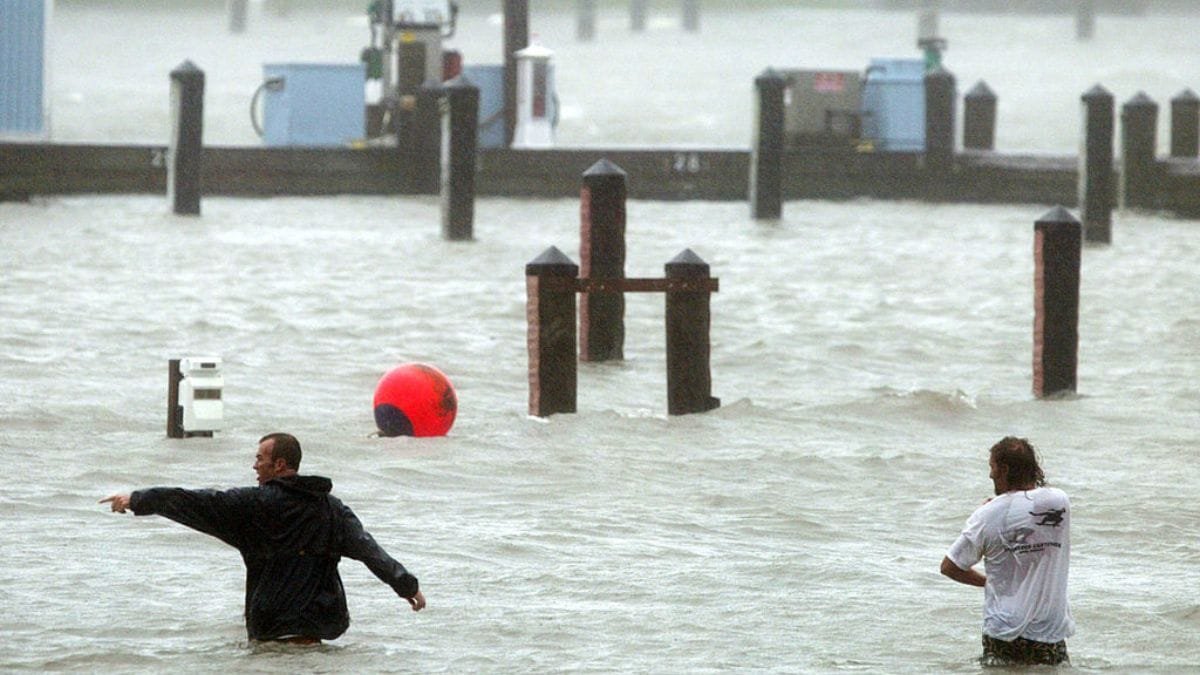

Nestled between Chesapeake Bay and the Atlantic Ocean, this popular tourist destination faces growing challenges. Storm surges regularly threaten coastal neighborhoods and businesses. Water levels rise faster here than almost anywhere else along the east coast. NOAA predictions show potential sea level increases of up to 12 feet by 2100. Hurricanes and nor’easters bring increasingly severe flooding to the area.
Local emergency services regularly conduct evacuation drills to prepare for future storms. Beach erosion threatens both tourism and residential areas. The marina district experiences regular flooding during high tides. City planners work to balance development with necessary flood protection measures. Residents must adapt to living with more frequent water-related disruptions.
The local economy depends heavily on finding ways to protect coastal attractions. Engineers study various options for protecting vulnerable infrastructure. Community leaders debate the best approaches for long-term sustainability.
#9. Indonesia Has A Plan To Relocate Jakarta, Which May Be Completely Underwater By 2050
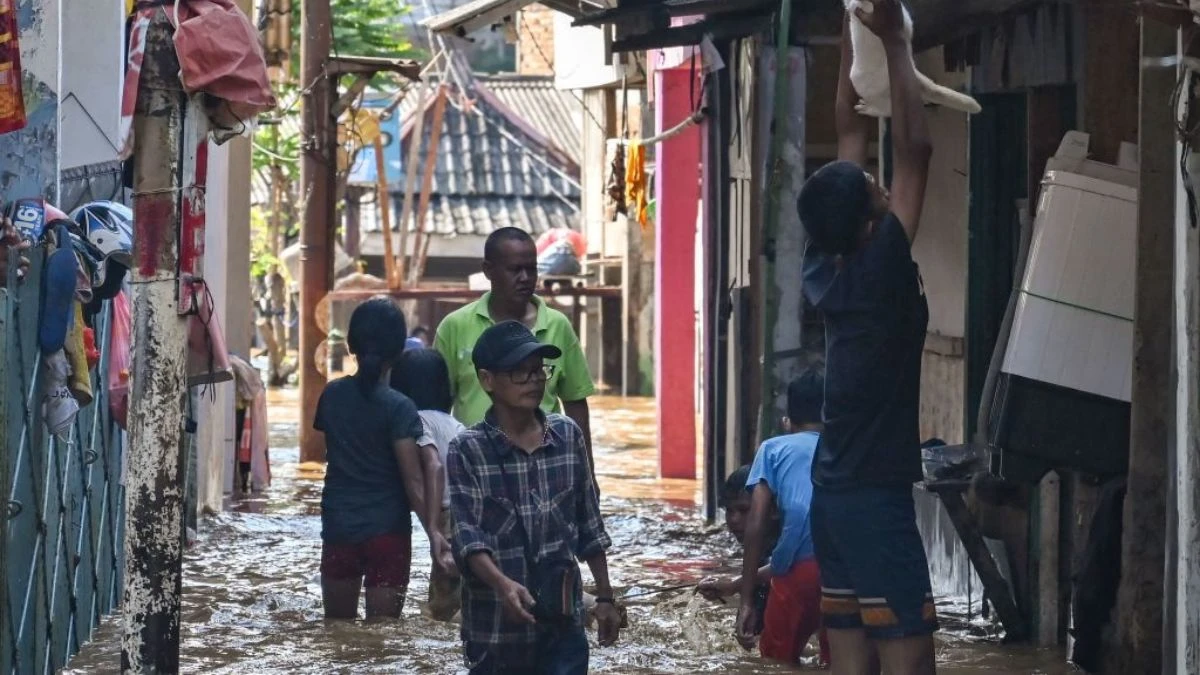

Sinking at an alarming rate of seven inches yearly, this massive city faces unprecedented challenges. Excessive groundwater pumping has destabilized the ground beneath millions of homes. Government officials have proposed an ambitious $33 billion relocation plan. The new capital city would be built 100 miles away from the current location.
Local communities struggle with increasing flood frequency and severity. Infrastructure damage costs the city billions in repairs and lost productivity. Residents in low-lying areas already experience regular flooding during rainy seasons. The massive relocation project would take at least a decade to complete. City planners face the enormous task of moving 10 million people to safer ground. Business leaders worry about economic impacts during the transition period.
Underground water extraction continues despite government restrictions. Many families cannot afford to relocate without government assistance. The situation highlights the growing impact of climate change on urban areas.
#10. A Rise In Sea Levels In Lagos, Nigeria, Will Produce A ‘Catastrophic Effect’

Africa’s largest city stands at the frontline of climate change impacts. Low coastlines make this bustling metropolis especially vulnerable to rising waters. University studies warn of severe consequences if sea levels rise three to nine feet. Heavy rains already overwhelm the city’s drainage system regularly.
Local communities adapt their daily routines around flooding seasons. The Ogun river frequently overflows, affecting thousands of residents. Global warming threatens to accelerate current flooding problems.
City officials struggle to protect vital infrastructure from water damage. The rapid population growth strains existing flood control measures. Scientists project worldwide sea levels could rise over 6.5 feet by 2100. Poor neighborhoods face the greatest risks from increasing flood events. Local businesses must frequently close during severe flooding. The economic hub of Nigeria requires massive infrastructure investments to survive. Community leaders call for international support to address these challenges.
#11. The People Of Dhaka, Bangladesh, Are Used To Flooding

Monsoon season brings constant challenges to this bustling metropolis. Water regularly fills the streets due to an inadequate drainage system. Poor neighborhoods suffer the most severe impacts from frequent flooding. Local residents have adapted their daily routines to cope with water-logged streets. The city’s rapid growth has outpaced infrastructure development.
Scientists warn that climate change will make flooding even more severe. Many homes lack proper protection against rising water levels. Workers often wade through knee-deep water to reach their jobs. The government struggles to implement effective flood control measures. Urban planners face difficult decisions about future development projects. Despite contributing very little to global emissions, the city bears heavy consequences.
By 2050, flood waters might claim up to 17% of the country’s land. Local communities have developed unique ways to continue daily life during floods. Emergency services work overtime during heavy rainfall periods. Business owners raise their shops’ floors to protect inventory from water damage.
#12. Bangkok, Thailand, Is Collecting Rainwater To Reduce Flooding
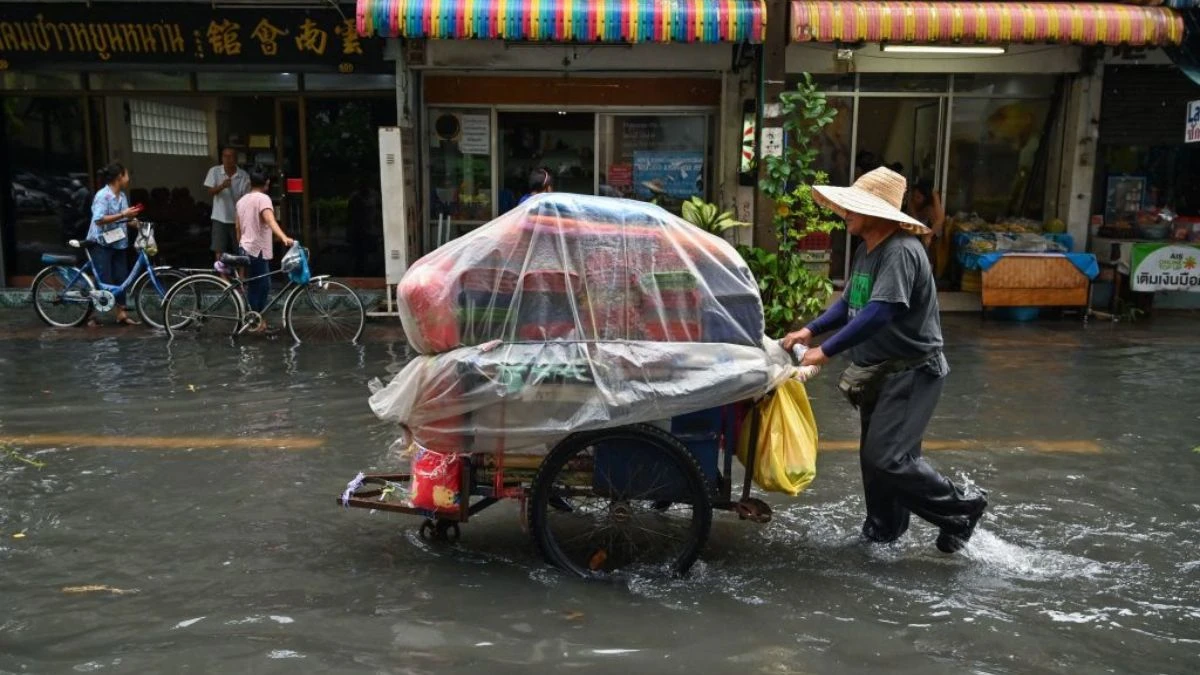

Innovative solutions help this Asian metropolis combat rising water levels. The city sinks more than one centimeter yearly, pushing engineers to find creative answers. An 11-acre park now serves as a giant water collector during heavy rains. Local authorities encourage buildings to create water storage systems. The summer season brings particular challenges to residents and businesses. Urban planners incorporate water management into new development projects.
The city might sink below sea level by 2030 without intervention. Community leaders promote water conservation awareness among residents. Architectural firms design buildings with flooding in mind. The combination of sinking land and rising seas threatens many neighborhoods. Parks and green spaces play crucial roles in flood prevention strategies.
Local markets adapt their structures to handle regular flooding. The city’s future depends on successfully managing water-related challenges. Traditional drainage systems struggle to handle increasing rainfall amounts. Business districts implement their own water management solutions.
#13. 90 Percent Of Rotterdam, The Netherlands, Is Below Sea Level
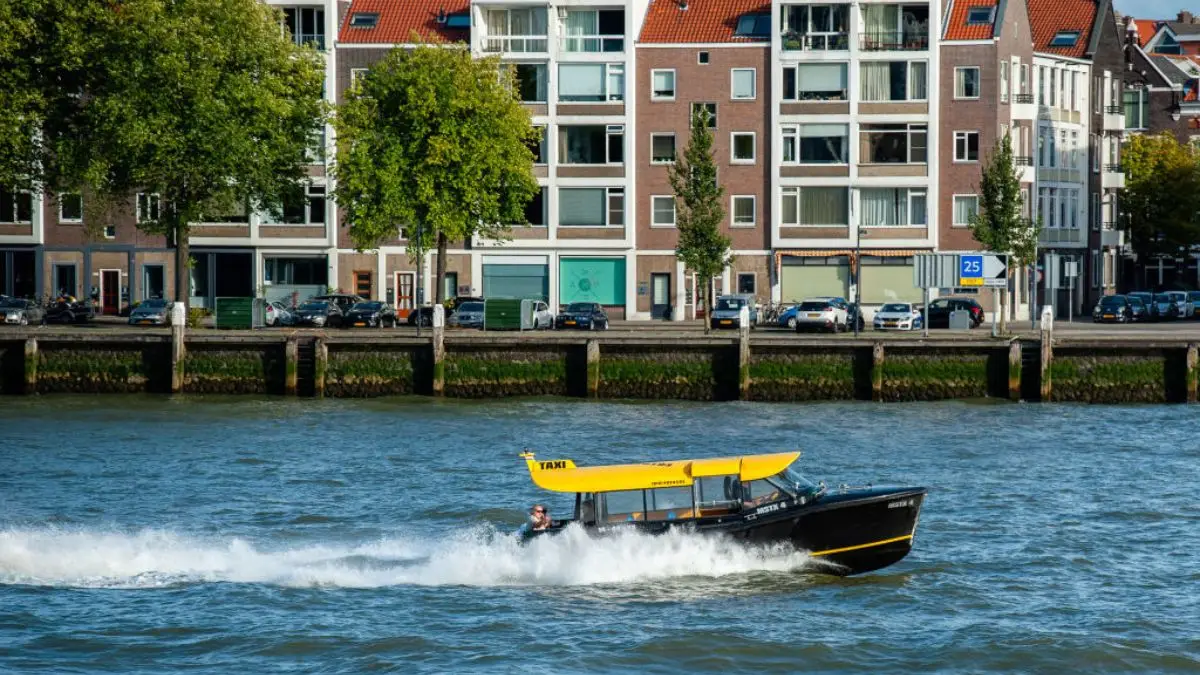

Dutch engineering prowess shines in this remarkable coastal city. Massive storm surge barriers protect millions of residents from flooding. The Maas River flows through carefully managed channels and barriers. Local parks double as water reservoirs during heavy rainfall. Engineers constantly monitor and upgrade flood protection systems. The port city’s economy depends on maintaining effective water management.
Residents live safely despite their precarious position below sea level. Advanced technology helps predict and prevent flooding events. The Dutch share their water management expertise with cities worldwide. Urban planning prioritizes flood protection in all new developments. Community involvement helps maintain and improve water management systems.
The city stands as an example of successful adaptation to environmental challenges. Local authorities invest heavily in flood prevention infrastructure. Schools teach children about living with water management systems. Rising ocean levels require continuous updates to protection measures.
#14. Rio De Janeiro, Brazil, Could Lose Its Famous Copacabana Beach
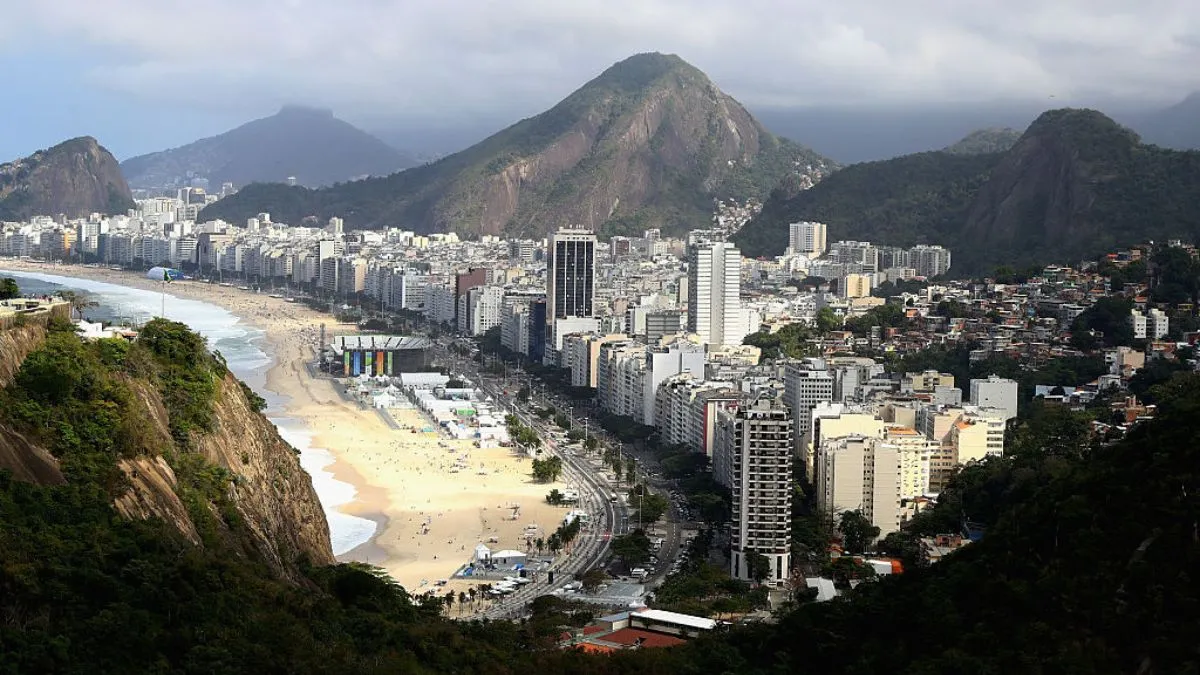

Rising temperatures threaten this South American beach paradise. Storm surges increasingly damage the iconic beachfront areas. A three-degree temperature increase could submerge famous coastal landmarks. The 2016 Olympic venue faces growing risks from flooding. Waterfront communities worry about property values and tourism impacts. Recent years have seen unprecedented damage to coastal infrastructure.
Local authorities scramble to protect popular beach areas from erosion. The airport’s location near the coast creates additional concerns. Storm damage regularly affects beachfront businesses and homes. Cliff erosion threatens both buildings and human safety. The city’s economy relies heavily on its famous beaches. Urban planners study various options for protecting coastal areas.
The combination of rising seas and stronger storms poses significant challenges. Tourism officials worry about long-term impacts on visitor numbers. Local communities debate the best approaches for coastal protection.
#15. The Beaches In Alexandria, Egypt, Are Disappearing

This ancient Mediterranean port faces modern environmental challenges. Water threatens both historical sites and modern infrastructure. The city handles most of Egypt’s national trade through its busy port. Coastal erosion steadily claims more of the famous beaches each year. Local authorities struggle to protect vital economic infrastructure.
The Mediterranean Sea could rise two feet by century’s end. Four million residents depend on effective flood protection measures. Storm surges increasingly threaten coastal neighborhoods and businesses. The industrial center requires extensive infrastructure upgrades. Historical buildings face damage from rising water levels. Local tourism suffers as beaches slowly vanish beneath waves.
The port’s economic importance makes protection measures crucial. Community leaders seek international support for adaptation projects. Scientists monitor sea level changes along the entire coastline. The city symbolizes broader challenges facing Mediterranean coastal areas.

