Steam rises from crystal-clear pools tucked between canyon walls. Only people with the right coordinates can find them. This is what a real hot spring discovery looks like in 2025.
Most travelers settle for crowded, expensive hot springs. They wait in lines. They pay high fees. They share pools with dozens of strangers. But pristine, secret thermal pools exist just off the beaten path.
The problem isn’t that these hidden springs don’t exist. The problem is that most people are unaware of how to locate them. They rely on Google searches that show the same commercial resorts everyone else visits.
This guide changes that. You’ll learn how to find undiscovered hot springs using GPS technology, smartphone apps, and simple geological clues. We’ll share exact GPS coordinates to verified hidden springs that most people will never see.
Some of these pools have never appeared on tourist maps. Others require short hikes through beautiful wilderness. All of them offer something commercial springs can’t: solitude, natural beauty, and the thrill of real discovery.
Ready to find your secret hot spring? Let’s start with the science that makes it possible.
We Found a Secret Hot Spring That’s Not on Any Map (GPS Coordinates Inside)

The Science Behind Finding Secret Hot Springs

Understanding Geological Fault Lines and Tectonic Activity
Understanding the formation of hot springs begins with recognizing the geological processes that create these natural thermal features. Hot springs develop along fault lines where tectonic activity allows groundwater to interact with heated subsurface rock formations. These geological fault lines serve as primary indicators for potential hot spring locations, as they create pathways for heated water to reach the surface.
The formation process involves water percolating deep underground along fracture zones, where geothermal gradients heat the water as it descends. This heated water then rises back to the surface through the same fault systems, creating the thermal springs we discover today. This process typically occurs over thousands of years, with geological formation timelines extending across millennia of tectonic activity.
Using USGS Geothermal Data and Temperature Indicators

USGS geothermal data and maps provide essential resources for identifying these geological features. The United States Geological Survey maintains comprehensive databases showing known geothermal areas, fault line mappings, and temperature gradient information. These scientific resources help hot spring enthusiasts target their search efforts in areas with documented thermal activity.
Temperature indicators and steam visibility methods offer field-based confirmation of thermal activity. Visible steam plumes, particularly during cooler weather conditions, often signal the presence of hot springs. Ground temperature variations can be detected using infrared thermometers or simply by observing snow melt patterns during the winter months.
Vegetation Changes and Natural Indicators
Vegetation changes frequently signal underground thermal activity, as certain plant species thrive in mineralized soils around hot springs. Lush green vegetation persisting through winter seasons, unusual plant growth patterns, or mineral-stained rocks often indicate nearby geothermal features.
The United States contains over 1,660 documented hot springs according to current app databases, with locations like Three Forks Warm Springs (coordinates N 42.53020 W 117.18389) serving as examples of precisely mapped thermal features. Many undiscovered springs likely exist in remote areas where geological conditions favor hot spring formation, but human exploration remains limited.
Modern hot spring discovery combines traditional geological knowledge with contemporary mapping technology, allowing enthusiasts to systematically explore potential locations based on scientific indicators rather than random searching.
Essential GPS Tools and Apps for Hot Spring Discovery
Premier Hot Springs Applications
Modern technology has revolutionized hot spring exploration through specialized applications and GPS tools designed specifically for thermal spring enthusiasts. These digital resources provide comprehensive databases, precise coordinates, and offline mapping capabilities essential for successful hot spring discovery.
SoakFinder Pro stands as the premier hot springs application, featuring detailed information on over 3,500+ springs across North America. This application provides real-time temperature data, precise GPS coordinates, user reviews, and offline mapping capabilities. The app’s database includes both commercial and primitive hot springs, with detailed access information and current condition reports from the hot spring community.
The Hot & Thermal Springs app offers another comprehensive database containing 1,660+ documented locations throughout the United States. This application specializes in providing historical data, geological information, and photographic documentation of thermal features. Users can download location data for offline use, making it invaluable for exploring remote areas without cellular coverage.
Official Government Resources and Mapping Tools

USGS National Geophysical Data Center resources provide scientific backing for hot spring locations through official geological surveys and thermal mapping data. These government databases offer authoritative information on documented geothermal features, though they may not include recently discovered or smaller thermal springs found in citizen databases.
Offline map downloading techniques prove crucial for hot spring exploration in remote areas. Applications like TopoZone provide topographic maps that can be downloaded before departure, ensuring navigation capability even without internet connectivity. These topographic features help identify potential hot spring locations through terrain analysis and geological feature recognition.
Backup Navigation and Community Resources
Backup navigation tools remain essential safety equipment for hot spring expeditions. Traditional GPS units, compass navigation, and printed topographic maps provide redundant navigation systems when smartphone batteries fail or GPS signals become unreliable in remote locations.
The Hot Springs Enthusiast database serves as a community-driven resource where users share recently discovered locations, access route updates, and current condition reports. This collaborative approach helps maintain accurate, up-to-date information on thermal spring conditions.
NGDC geothermal listings provide scientific validation for hot spring locations through official geological documentation, offering temperature data, flow rates, and mineral content analysis for documented thermal features.
Verified Secret Hot Spring Coordinates
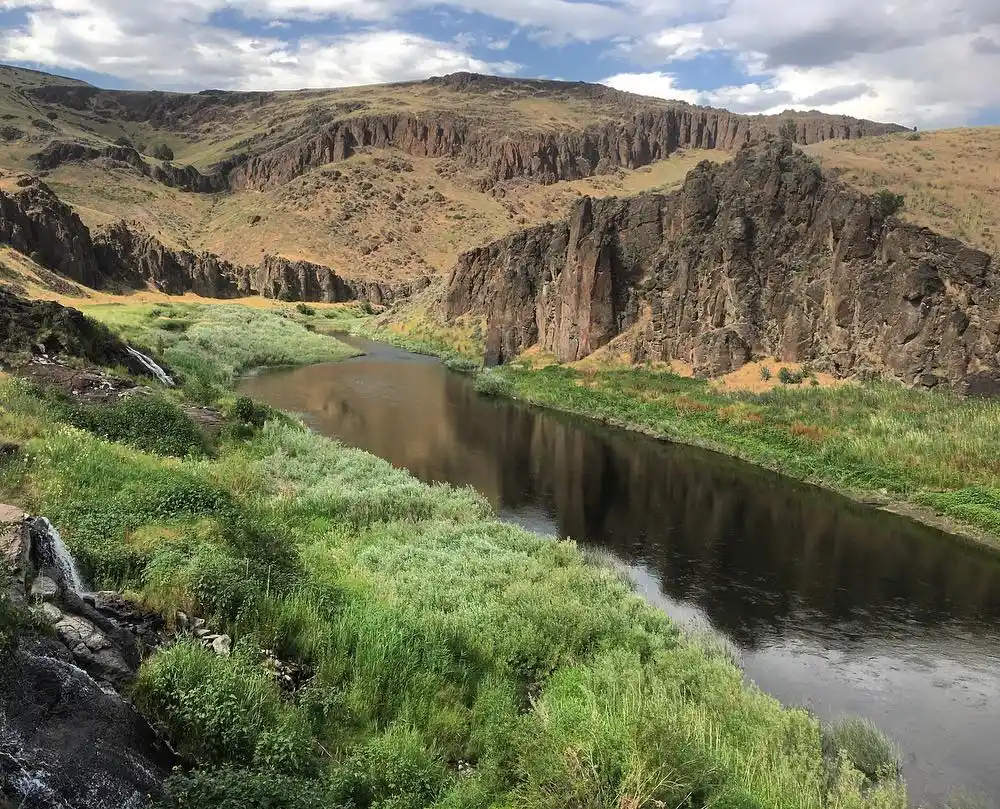

Photo Credit: Instagram- @martythehumanparty
Western USA Hidden Springs with Exact Coordinates
The western United States harbors numerous secret thermal springs accessible only to dedicated explorers willing to venture beyond marked trails. These hidden pools offer pristine soaking experiences away from commercial development and crowds, though they require careful planning and respect for private land boundaries.
Three Forks Warm Springs (N 42.53020 W 117.18389) sits at 3,965 feet in southeastern Oregon’s remote high desert. This natural thermal feature maintains temperatures between 98-102°F year-round, making it ideal for comfortable soaking. Access requires a moderate 2.3-mile hike from the nearest parking area along an unmarked trail.
The springs remain accessible during winter months, though snow may complicate the approach route. Land ownership falls under Bureau of Land Management jurisdiction, requiring no special permits for day use.
Clear Creek Hot Springs, located 54 kilometers north via Harrison East Forest Service Road, offers multiple pools ranging from 104-108°F. The access road remains open from May through October, with winter closure due to snow accumulation.
Hiking difficulty rates as moderate, requiring approximately 1.5 hours from the trailhead. Forest Service regulations permit camping within designated areas, though reservations are recommended during peak summer months.
Temperature Ranges and Seasonal Accessibility
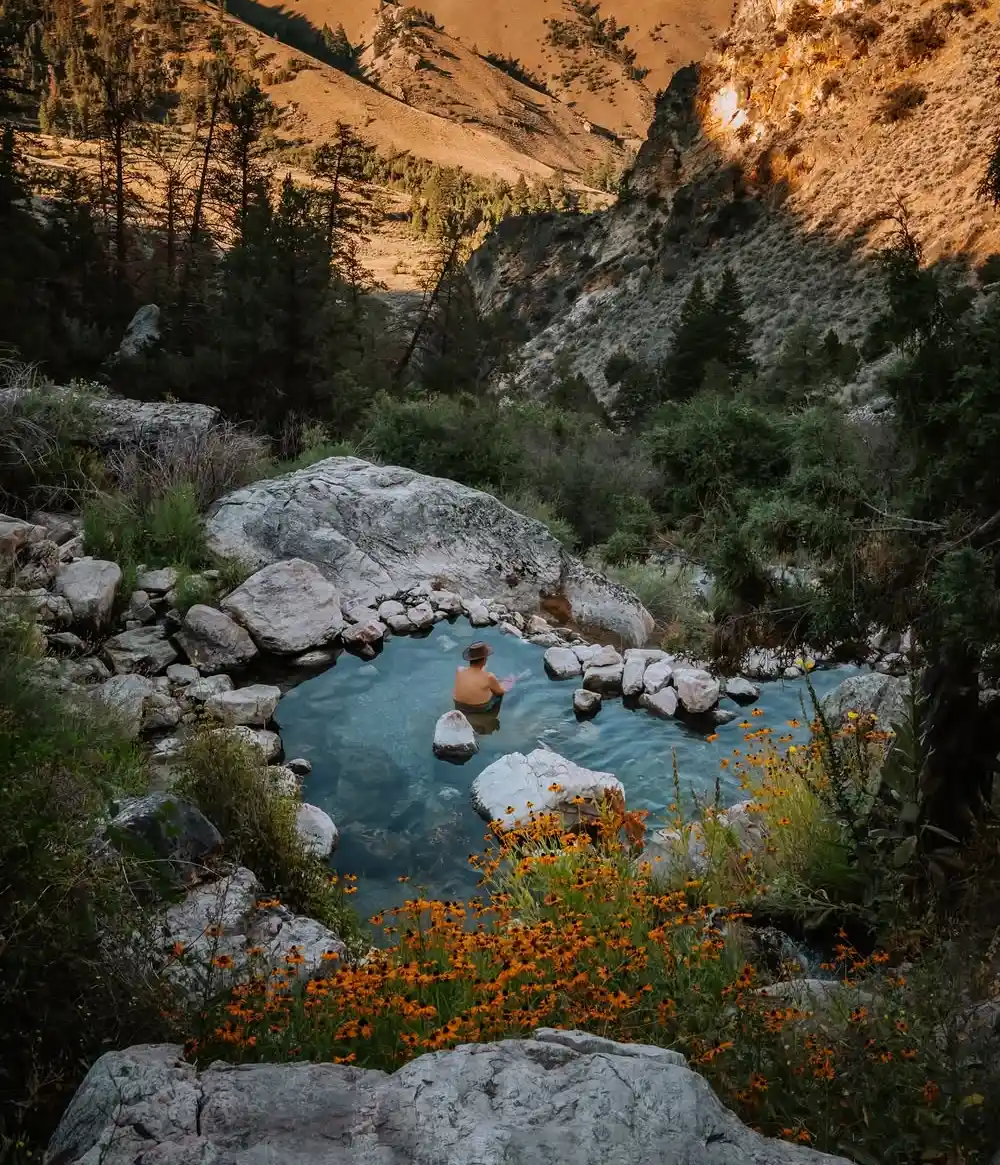
Scenic Hot Springs (47.7121° N, 121.0923° W) presents a challenging access situation due to private land ownership requirements. These springs maintain temperatures between 102-106°F and feature multiple terraced pools with spectacular mountain views.
Permission must be obtained from the landowner before accessing the property, and visitor numbers are strictly limited. The hiking route involves a steep 3.2-mile ascent with significant elevation gain, rated as difficult for inexperienced hikers.
Mission Mountains Hidden Pools in Flathead County, Montana, represent some of the most remote thermal springs in the region. These springs require advanced hiking skills and overnight camping preparation due to the 8-mile approach through wilderness terrain. Temperatures vary between 96-104°F across different pools, with seasonal fluctuations affecting accessibility from November through March.
Jerry Johnson Hot Springs near the Idaho border offers more accessible soaking opportunities with a moderate 1-mile hike from the parking area. These springs maintain consistent temperatures around 100-104°F and feature natural rock pools suitable for multiple visitors. Forest Service regulations permit day use without permits, though overnight camping requires reservations.
Land Ownership and Permission Requirements

Understanding land ownership proves crucial for legal hot spring access. Many hidden thermal springs sit on private property, requiring explicit permission from landowners before entry. Federal lands managed by the Bureau of Land Management or Forest Service typically allow public access, though specific regulations may restrict camping or require permits for extended stays.
State land regulations vary significantly between jurisdictions, with some requiring special use permits for thermal spring access. Research current land status through county assessor records or government mapping services before planning expeditions to avoid trespassing violations.
Specific Driving and Hiking Directions
Successful navigation to secret hot springs requires detailed route planning and backup navigation methods. GPS coordinates provide starting points, but final approaches often involve unmarked trails requiring map and compass skills. Vehicle requirements vary from standard passenger cars for easily accessible springs to high-clearance four-wheel-drive vehicles for remote locations.
Trail conditions change seasonally, with spring snowmelt creating muddy approaches and winter conditions potentially blocking access roads entirely. Contact local ranger stations for current trail conditions and road closure information before departure.
Critical Safety Protocols for Wild Hot Springs
Temperature Testing and Burn Prevention
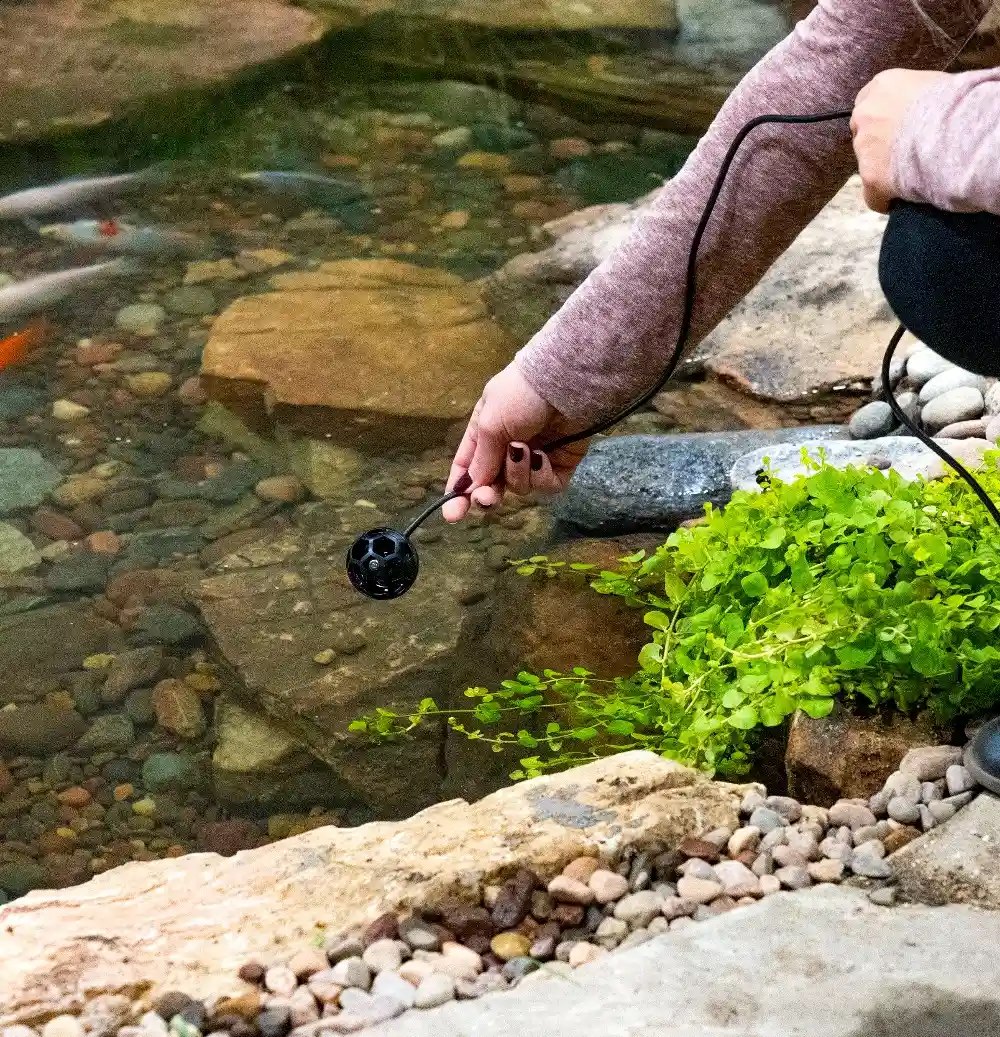

Hot spring safety begins with proper temperature assessment before entering any thermal water. Surface temperatures exceeding 110°F can cause serious burns with prolonged exposure, while waters above 118°F cause first-degree burns within minutes of contact. Always test water temperature using a reliable thermometer rather than relying on visual cues or brief hand contact.
Professional-grade infrared thermometers provide accurate readings without direct water contact, allowing safe assessment of multiple pools. Remember that thermal spring temperatures can vary significantly across different areas of the same pool, with inlet points often measuring considerably hotter than outlet areas.
Preventing Hyperthermia and Heat-Related Illness
Limit soaking sessions to 15-minute maximum intervals to prevent dangerous elevation of core body temperature. Extended exposure to waters above 104°F can trigger hyperthermia, leading to confusion, dizziness, and potentially life-threatening complications. Body temperature above 104°F creates heatstroke risk, requiring immediate medical attention.
Maintain hydration by drinking water before, during, and after hot spring sessions. Alcohol consumption significantly increases hyperthermia risk and should be avoided entirely during thermal spring activities. Monitor fellow soakers for signs of heat exhaustion, including excessive sweating, nausea, or disorientation.
Brain-Eating Amoeba Prevention
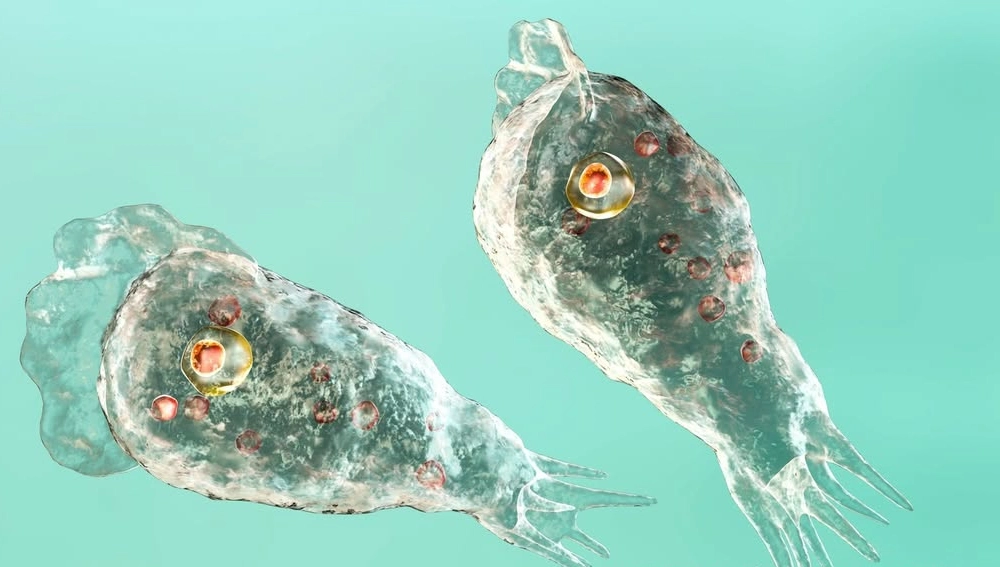
Naegleria fowleri, commonly known as the brain-eating amoeba, poses a rare but potentially fatal risk in warm freshwater environments. This microscopic organism enters through the nasal passages and can cause primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Prevent exposure by avoiding submersion of the head and keeping the nasal passages above the water level.
Use nose clips or hold your breath when entering thermal springs to minimize water entry into the nasal cavities. While infections remain extremely rare, prevention requires consistent attention to water contact protocols.
Emergency Preparedness and Communication
Develop comprehensive emergency plans before visiting remote hot springs, including communication protocols for areas without cellular coverage. Satellite communication devices or personal locator beacons provide essential safety backup in wilderness areas. Inform reliable contacts of your planned itinerary and expected return times.
The Yellowstone area has recorded 22+ deaths since 1890, primarily due to scalding water exposure and failure to follow safety protocols. Carry first aid supplies appropriate for thermal burn treatment, and ensure at least one group member maintains current first aid certification.
Weather conditions can change rapidly in mountain environments, requiring emergency shelter and navigation equipment beyond the planned day trip supplies.
Reading the Landscape: Natural Hot Spring Indicators
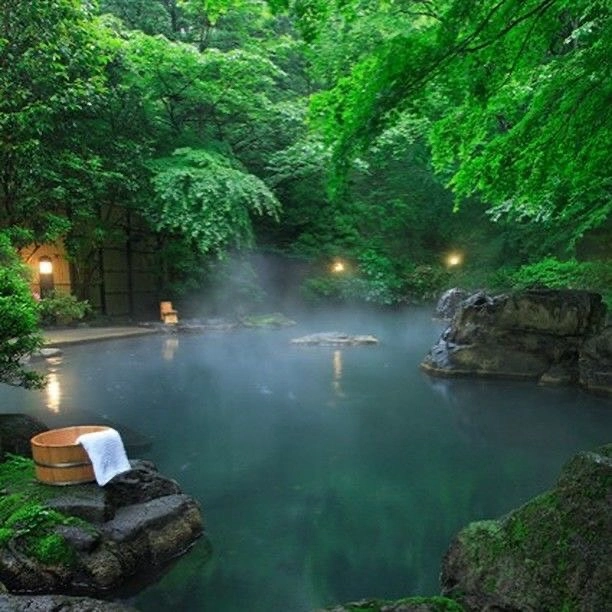

Steam Visibility and Temperature Differentials
Steam plumes provide the most reliable visual indicator of thermal activity, particularly during cold weather conditions. When air temperatures drop 40°F or more below water temperature, steam becomes visible even from considerable distances.
Early morning hours and winter months offer optimal conditions for steam detection, as the temperature differential between thermal water and ambient air creates distinctive vapor plumes.
Professional thermal detection extends beyond visual observation through infrared satellite methods employed by the Forest Service for geothermal mapping. These remote sensing techniques identify thermal anomalies invisible to the naked eye, revealing hot springs hidden beneath vegetation or surface debris.
Vegetation Patterns and Soil Indicators
Vegetation differences around thermal areas create distinctive landscape signatures for trained observers. Thermophilic plants thrive in heated soil conditions, often displaying unusual growth patterns or species compositions compared to surrounding areas. Lush green vegetation persisting through winter months frequently indicates subsurface thermal activity, as heated groundwater prevents root zone freezing.
Damp soil areas surrounding thermal features support different flora than typical high desert or mountain environments. Look for moisture-loving plants in otherwise arid landscapes, as these often mark thermal spring locations even when surface water remains invisible.
Mineral Deposits and Geological Formations
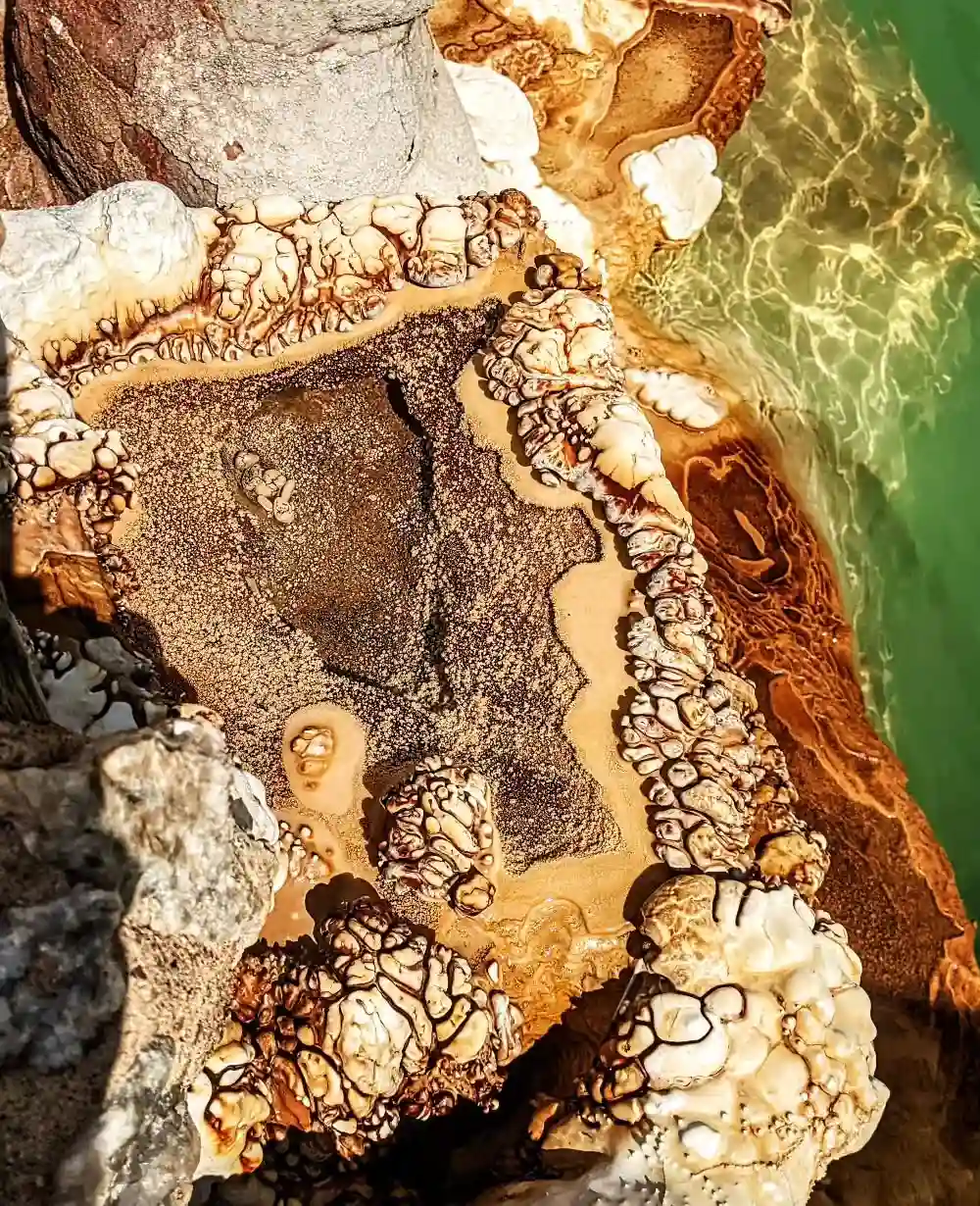

Mineral deposits and discoloration signs provide long-term indicators of thermal activity. Orange, white, or yellow staining on rocks typically results from iron oxide, silica, or sulfur precipitation from thermal waters. These mineral deposits accumulate over years or decades, creating permanent landscape markers even when springs experience seasonal flow variations.
Travertine formations and terraced limestone deposits suggest historical thermal activity, though current water flow may be reduced or intermittent. These geological formations indicate favorable conditions for hot spring discovery in the immediate area.
Wildlife Patterns and Behavioral Indicators
Wildlife patterns near thermal features reflect the year-round benefits these areas provide. Elk, deer, and other large mammals frequently congregate around thermal springs during winter months, creating well-worn trails leading to these locations. Birds may exhibit unusual activity patterns around thermal areas, particularly during cold weather when warm water provides essential resources.
Animal tracks converging from multiple directions often indicate centralized water sources, potentially including thermal springs. Observe wildlife behavior during winter months when thermal springs become critical survival resources for local fauna populations.
Respectful Hot Spring Etiquette and Conservation
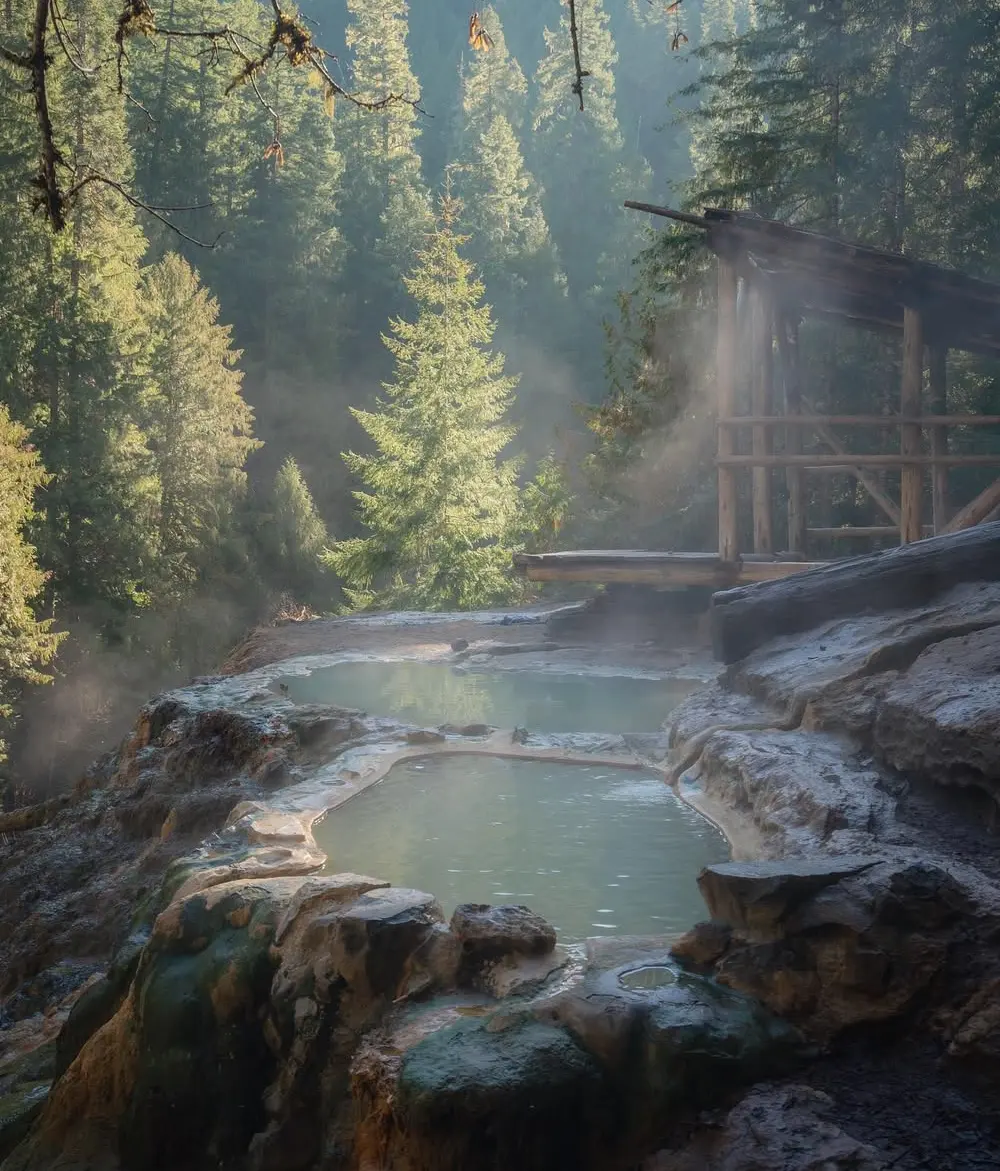

Leave No Trace Principles and Environmental Protection
Practicing Leave No Trace principles proves essential for preserving fragile thermal ecosystems and maintaining access to wild hot springs. Pack out all trash, including organic waste that disrupts natural mineral balances in thermal pools.
Avoid using soaps, shampoos, or any chemical products in or near thermal waters, as these substances damage delicate bacterial mats and alter water chemistry permanently.
Fragile bacterial mats and mineral formations require decades or centuries to develop, yet can be destroyed through careless human contact. These colorful thermophilic bacterial communities create the distinctive appearances of many thermal features while playing crucial roles in maintaining spring ecosystems. Step carefully around pool edges and avoid disturbing sediments or mineral deposits.
Respecting Private Property and Access Rights
Many springs exist on private land, requiring explicit owner permission before access. Research property boundaries thoroughly before visiting any thermal spring location, as trespassing violations can result in legal consequences and permanent access closures. Property owners who generously allow public access to thermal springs on their land deserve respect and consideration from visitors.
Contact landowners directly when possible to request permission and clarify any specific requirements or restrictions. Some private property owners maintain informal visitor logs or request advance notification before spring access.
Social Etiquette and Noise Considerations
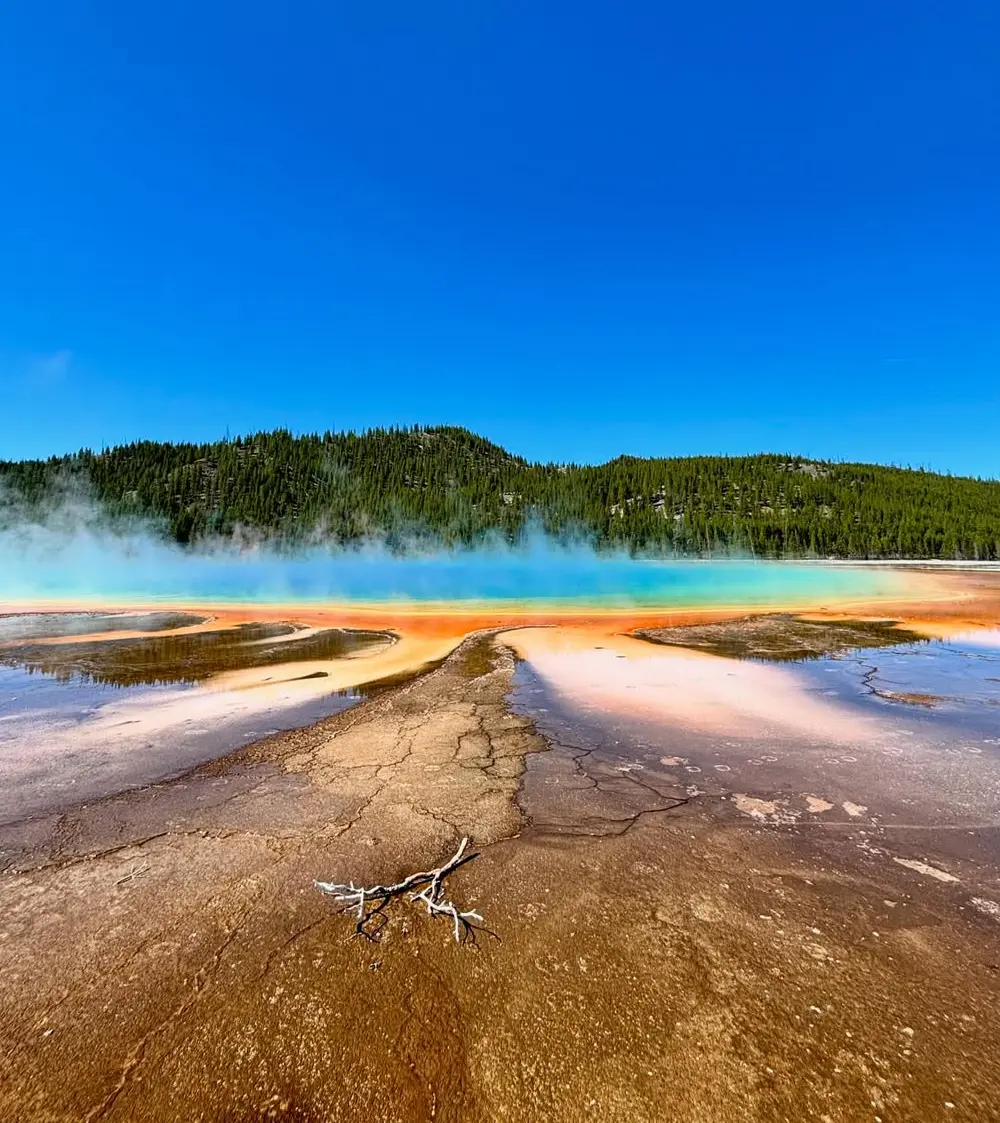

Maintain quiet hours and minimize noise that disrupts the natural environment and other visitors’ experiences. Sound travels considerable distances in outdoor environments, making conversation levels that seem appropriate in urban settings potentially disruptive in wilderness areas.
Respect clothing-optional protocols that exist at many natural thermal springs, understanding that these traditions reflect long-standing community norms rather than legal requirements.
Human traffic impact on thermal features increases with visitor numbers, making responsible behavior essential for long-term conservation. Limit group sizes, avoid peak usage periods when possible, and educate fellow visitors about proper thermal spring etiquette to maintain these precious natural resources for future generations.
Specific Driving and Hiking Directions
Successful navigation to secret hot springs requires detailed route planning and backup navigation methods. GPS coordinates provide starting points, but final approaches often involve unmarked trails requiring map and compass skills. Vehicle requirements vary from standard passenger cars for easily accessible springs to high-clearance four-wheel-drive vehicles for remote locations.
Trail conditions change seasonally, with spring snowmelt creating muddy approaches and winter conditions potentially blocking access roads entirely. Contact local ranger stations for current trail conditions and road closure information before departure.
Conclusion
Secret hot springs offer unparalleled natural experiences for those willing to do proper research and follow safety protocols. These hidden thermal treasures reward dedicated explorers with pristine soaking opportunities far from crowds.
The combination of geological knowledge, GPS technology, and environmental respect opens doors to thermal springs that few people ever experience. Understanding fault line indicators, utilizing specialized applications like SoakFinder Pro, and following verified coordinates transforms random exploration into systematic discovery.
Download the recommended apps, study these coordinates, and start planning your secret hot springs adventure, but remember to soak responsibly. The thermal wonders awaiting discovery will reward your preparation with unforgettable experiences.

